Kia Sedona: CVVT (Continuous Variable Valve Timing) System Description and Operation
Kia Sedona: CVVT (Continuous Variable Valve Timing) System Description and Operation
Third generation YP (2014-2026) / Kia Sedona YP Service Manual / Emission Control System / Exhaust Emission Control System / CVVT (Continuous Variable Valve Timing) System Description and Operation
| Description |
Continuous Variable Valve Timing (CVVT) system advances or
retards the valve timing of the intake and exhaust valve in accordance
with the ECM control signal which is calculated by the engine speed and
load.
By controlling CVVT, the valve over-lap or under-lap occurs,
which makes better fuel economy and reduces exhaust gases (NOx, HC).
CVVT improves engine performance through reduction of pump loss,
internal EGR effect, improvement of combustion stability, improvement of
volumetric efficiency, and increase of expansion work.
This system consists of:
| – |
the CVVT Oil Control Valve (OCV) which supplies the engine
oil to the cam phaser or runs out the engine oil from the cam phaser in
accordance with the ECM PWM (Pulse With Modulation) control signal, |
| – |
the CVVT Oil Temperature Sensor (OTS) which measures the engine oil temperature, |
| – |
and the Cam Phaser which varies the cam phase by using the hydraulic force of the engine oil. |
The engine oil released from the CVVT oil control valve
varies the cam phase in the direction (Intake Advance/Exhaust Retard) or
in the opposite direction (Intake Retard/Exhaust Advance) of the engine
rotation by rotating the rotor connected to the camshaft inside the cam
phaser.
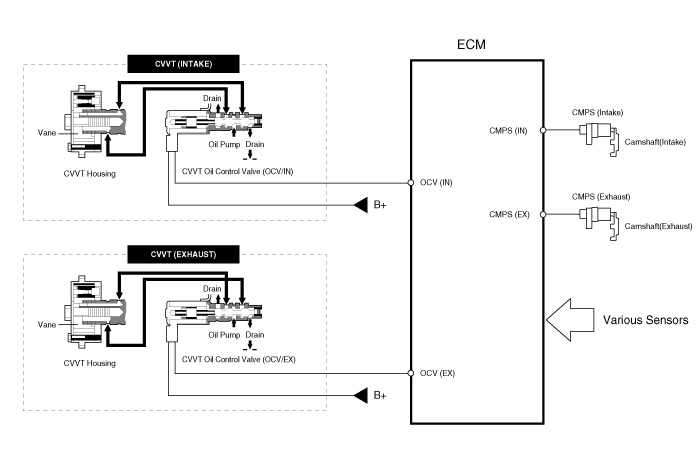
| Operation Principle |
The CVVT has the mechanism of rotating the rotor vane with
hydraulic force generated by the engine oil supplied to the advance or
retard chamber in accordance with the CVVT oil control valve control.
| [CVVT System Mode] |
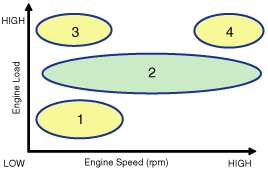
| (1) Low Speed / Low Load | (2) Partial Load |
|
|
| (3) Low Speed / High Load | (4) High Speed / High Load |
|
|
| Driving Condition | Exhaust Valve | Intake Valve | ||
| Valve Timing | Effect | Valve Timing | Effect | |
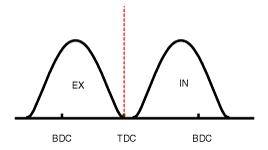
| (1) Low Speed /Low Load | Completely Advance | * Valve Under-lap * Improvement of combustion stability | Completely Retard | * Valve Under-lap * Improvement of combustion stability |
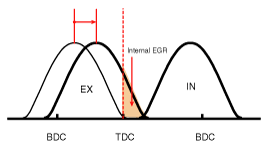
| (2) Part Load | Retard | * Increase of expansion work * Reduction of pumping loss * Reduction of HC | Retard | * Reduction of pumping loss |
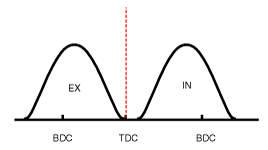
| (3) Low Speed /High Load | Retard | * Increase of expansion work | Advance | * Prevention of intake back flow (Improvement of volumetric efficiency) |
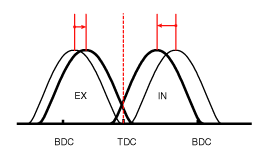
| (4) High Speed /High Load | Advance | * Reduction of pumping loss | Retard | * Improvement of volumetric efficiency |
 Catalytic Converter Repair procedures
Catalytic Converter Repair procedures
Removal
[Catalytic Converter (WCC)]
1.
Remove the exhaust manifold.
(Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Exhaust Manifold")
[Catalytic Converter (UCC)]
1.
Remove the Center Muffler. ...
Other Information:
General Information
General Service Information
Protection Of The Vehicle
Always be sure to cover fenders, seats, and floor areas before starting work.
The support rod must be inserted i ...
Battery Description and Operation
Description
1.
The CMF(Closed Maintenance Free) battery is, as the name
implies, totally maintenance free and has no removable battery cell
caps.
2.
The CMF(Closed Maintenance Free) batter ...
Categories
- Home
- First Generation
- Second Generation
- Third generation
- Kia Sedona YP 2014-2026 Owners Manual
- Kia Sedona YP 2014-2026 Service Manual
Copyright © www.kisedona.com 2016-2026